Introduction
The human auditory system is a marvel of nature, responsible for connecting us with the world of sounds. From the soft rustle of leaves to the crescendo of a symphony, our ears play an integral role in how we experience life. However, for many adults, this connection is disrupted due to a condition known as sensorineural hearing loss. A complex and often misunderstood disorder, it stands as the most common form of hearing loss. This post will delve into the intricate world of sensorineural hearing loss, focusing on cutting-edge research, potential treatments, and the factors that contribute to this condition. Our aim is to inform and educate, providing a resource that caters directly to adults with sensorineural hearing loss.
Cutting-Edge Research: The Hunt for a Cure for Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The quest for a cure for sensorineural hearing loss is ongoing, with researchers worldwide dedicating their efforts to this cause. Current research is multi-faceted, focusing on diverse areas from gene therapy to bioengineered solutions. For instance, one promising area of study revolves around the regeneration of damaged hair cells within the cochlea, the part of the inner ear responsible for converting sound vibrations into nerve signals. When these hair cells are damaged, sensorineural hearing loss occurs. Yet, recent advancements suggest that it might be possible to stimulate the regeneration of these cells, potentially reversing the effects of sensorineural hearing loss.
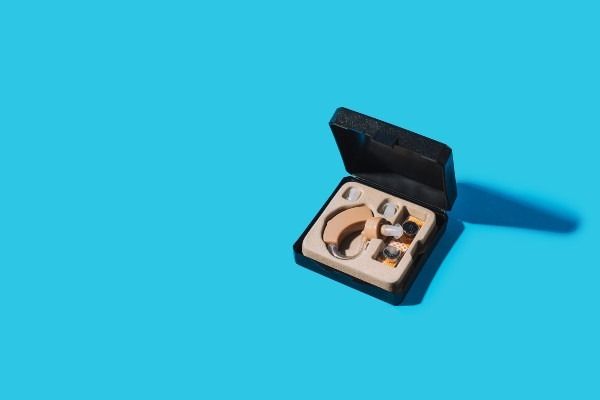
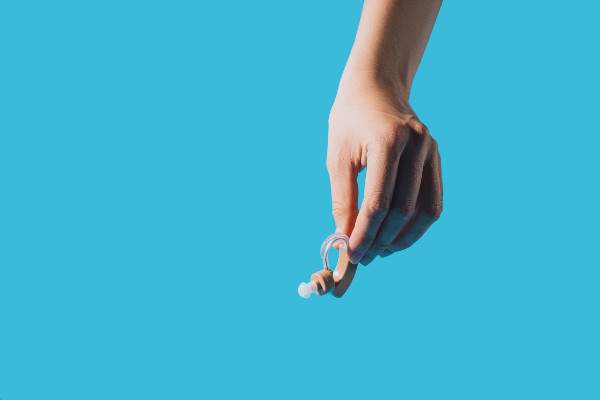
OTC Hearing Aid Pair
Experience the world like never before with the RCA OTC Behind-the-Ear Hearing Aid. Our advanced digital technology ensures that every sound is crystal clear and vibrant, allowing you to fully immerse yourself in life’s experiences. Whether it’s the laughter of loved ones or the music that moves you, our hearing aid brings back the joy of every moment.
Say goodbye to the hassle of appointments and prescriptions. The RCA OTC Hearing Aid is designed to meet the needs of individuals without the need for a prescription. With its seamless setup and user-friendly design, you can effortlessly enhance your hearing abilities and stay connected to the world around you. Simply unpack, wear, and enjoy improved auditory perception instantly.
Experience optimal comfort and style with our discreet behind-the-ear design. The thin tube design allows you to wear glasses comfortably, so you can enjoy clear hearing while maintaining your personal sense of style. Plus, our rechargeable battery ensures long-lasting power, eliminating the inconvenience of constantly replacing small batteries. Elevate your hearing experience with the RCA OTC Hearing Aid and embrace the world with confidence.
Can Stem Cells Reverse Sensorineural Hearing Loss? Current Studies
Building on the idea of cell regeneration, stem cell therapy presents a promising avenue in the fight against sensorineural hearing loss. Stem cells, known for their ability to transform into a variety of cell types, offer potential in regenerating the damaged hair cells within the inner ear. Preliminary studies have yielded positive results. For example, a study published in the Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology demonstrated that transplanted stem cells could successfully grow to resemble native hair cells in mice, indicating a potential application in human therapy.
SUDDEN HEARING LOSS – SYMPTOMS, CAUSES AND TREATMENTS
The Anatomy of the Ear: Inner Workings and Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Diving deeper into the intricacies of sensorineural hearing loss requires a foundational understanding of the inner workings of our ears. The ear is divided into three primary sections: the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear captures sound waves, directing them into the ear canal. The sound waves then reach the middle ear, causing the eardrum to vibrate. This vibration is transferred to the ossicles, three tiny bones that amplify the sound and send it to the inner ear.
In the inner ear resides a spiral-shaped structure called the cochlea, filled with fluid and lined with thousands of tiny hair cells. These hair cells move with the fluid’s vibrations, creating electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain through the auditory nerve, allowing us to interpret the sounds. Sensorineural hearing loss primarily arises from damage to these hair cells or the auditory nerve itself. Understanding this mechanism is vital, as it paves the way for potential treatments targeting these specific structures.
Exploring the Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children
Sensorineural hearing loss is not confined to adults; it also significantly impacts children’s lives. Several factors contribute to this condition in younger demographics. Genetic factors often play a pivotal role. Certain genetic mutations can cause hearing loss at birth or progressive hearing loss as the child grows. Infections during pregnancy, such as rubella or cytomegalovirus, can also result in sensorineural hearing loss in the child.
Furthermore, premature birth is another significant factor, with premature babies having a higher risk of sensorineural hearing loss. Noise exposure, though less common in children than in adults, can also lead to this condition. It’s crucial to raise awareness about these causes to facilitate early detection and intervention, potentially improving the quality of life for children affected by sensorineural hearing loss.
Tinnitus: why it’s still such a mystery to science
Noise-Induced Sensorineural Hearing Loss: An In-Depth Look
One specific cause of sensorineural hearing loss that warrants closer examination is noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). Exposure to excessive noise levels over an extended period or even a single traumatic event can lead to permanent damage to the inner ear, resulting in sensorineural hearing loss. Occupational noise, recreational activities, and environmental factors all contribute to the risk of developing NIHL.
Understanding the mechanisms of NIHL can help individuals take proactive measures to protect their hearing. The loudness of sound is measured in decibels (dB), and prolonged exposure to sounds above 85 dB can be detrimental. For example, working in a construction site, attending loud concerts, or using high-volume headphones for extended periods can all increase the risk of NIHL.
Prevention is crucial when it comes to noise-induced sensorineural hearing loss. Implementing strategies such as using hearing protection devices (such as earplugs or earmuffs) in noisy environments, maintaining safe listening levels during recreational activities, and creating awareness about the importance of hearing conservation can significantly reduce the incidence of NIHL.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration of sensorineural hearing loss, we have delved into cutting-edge research efforts, examining potential cures and the promise of stem cell therapy. We have explored the intricate anatomy of the ear, providing insight into how sensorineural hearing loss occurs at a cellular level. Additionally, we have highlighted the causes of sensorineural hearing loss in children, emphasizing genetic factors and the impact of noise exposure. Lastly, we have shed light on noise-induced hearing loss and the importance of preventative measures.
Sensorineural hearing loss poses unique challenges, but with advancements in research and technology, there is hope for improved treatments and interventions. By raising awareness, fostering understanding, and advocating for hearing health, we can empower individuals with sensorineural hearing loss to live fulfilling lives. Remember, early detection, timely interventions, and proactive hearing conservation are essential in the journey towards better hearing and quality of life.