Introduction
Lipo-Flavonoid Plus, Tinnitus Relief for Ringing Ears
Considered the most effective over-the-counter solution by ENTs, this product comes highly recommended by doctors for reducing ear ringing. Its effectiveness has been acknowledged and trusted by medical professionals in the field.
Please note that exposure to heat or sunlight may cause melting or damage to the product. To ensure the product’s integrity, customers are advised to be present during the delivery process.
Formulated with a natural lemon bioflavonoid complex, this product contains a rich blend of essential vitamins and nutrients such as Vitamins C, B1, B2, B6, B12, Calcium, Choline Bitartrate, Inositol, Niacin, and Pantothenic Acid. These ingredients provide vital nutritional support for the inner ear, making it beneficial for individuals with tinnitus and Meniere’s syndrome.
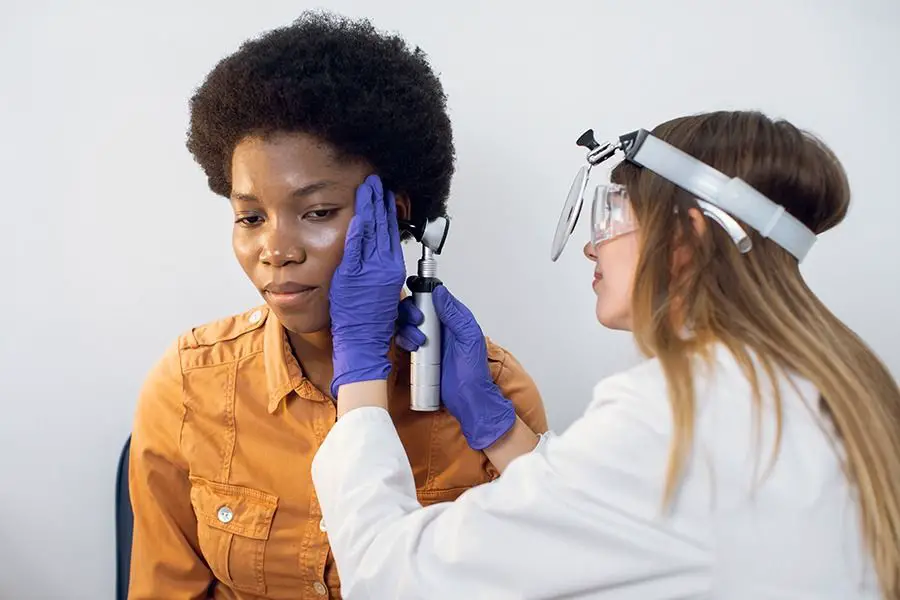
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Identifying Hearing Loss as a Symptom of Meningitis Hearing loss can be a significant symptom of meningitis, and recognizing it promptly is vital for timely intervention. It is important to be vigilant of any changes in a person’s ability to hear, especially if they have recently experienced symptoms of meningitis such as high fever, severe headache, neck stiffness, and sensitivity to light. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) highlights that “hearing loss may develop quickly or over several days” following the onset of meningitis symptoms.
One example that illustrates the connection between meningitis and hearing loss is the case of James, a 10-year-old boy who developed bacterial meningitis. His parents initially noticed his declining responsiveness to conversations, television, and everyday sounds. They immediately sought medical attention, and James was diagnosed with meningitis-related hearing loss. The timely recognition of hearing loss allowed for early intervention, including the use of hearing aids and speech therapy, enabling James to regain communication skills and participate fully in school and social activities.
Acute vs. Chronic Hearing Loss in Meningitis Patients
Meningitis-related hearing loss can manifest as either acute or chronic. Acute hearing loss refers to a sudden and severe loss of hearing, typically occurring soon after the onset of meningitis. On the other hand, chronic hearing loss may develop gradually over time, appearing weeks or even months after the infection. The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom emphasizes that both acute and chronic hearing loss can have significant long-term consequences if left untreated.
An example that demonstrates the distinction between acute and chronic hearing loss in meningitis patients is the case of Emma, a 27-year-old woman who contracted viral meningitis. Initially, Emma experienced mild hearing loss, which gradually worsened over several months. She initially dismissed it as a temporary side effect of the infection, but her symptoms persisted. After seeking medical advice, Emma was diagnosed with chronic hearing loss resulting from meningitis. Her journey towards rehabilitation involved the use of hearing aids and auditory training, allowing her to regain confidence in her ability to communicate effectively.
Diagnostic Tools and Tests for Meningitis-Induced Hearing Loss
Diagnostic tools and tests play a crucial role in confirming and evaluating meningitis-induced hearing loss. When a caregiver suspects hearing loss as a result of meningitis, it is essential to consult with an audiologist or an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist) who can conduct a comprehensive evaluation.
One of the primary diagnostic tools used is pure-tone audiometry, a test that measures an individual’s hearing sensitivity across different frequencies. This test helps determine the degree and configuration of hearing loss, whether it is conductive (related to the middle ear), sensorineural (related to the inner ear or auditory nerve), or mixed (a combination of both). Another valuable tool is tympanometry, which assesses the function of the middle ear and helps identify any abnormalities or blockages.
For more detailed evaluations, additional tests may be conducted, such as speech audiometry and otoacoustic emissions (OAE) testing. Speech audiometry assesses an individual’s ability to understand and discriminate speech sounds, providing valuable insights into the impact of hearing loss on communication. OAE testing measures the sounds generated by the inner ear in response to stimulation, helping to assess the function of the cochlea.
FAQ – Hearing Loss: what you need to know
Evaluating Meningitis-Related Hearing Loss in Children and Adults
The evaluation and management of meningitis-related hearing loss can differ between children and adults. In pediatric cases, early identification and intervention are particularly critical due to the potential impact on language and cognitive development. The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) emphasizes the importance of conducting hearing screenings for children who have had meningitis to detect any hearing loss as early as possible.
Children may undergo play audiometry, a method that uses age-appropriate activities and games to assess their hearing abilities. Visual reinforcement audiometry and conditioned play audiometry are commonly used techniques to evaluate hearing in young children who may not be able to provide reliable responses. Additionally, speech-language pathologists play a crucial role in assessing language development and providing therapy services for children with meningitis-induced hearing loss.
In adults, a comprehensive audiological assessment is performed to determine the extent and nature of hearing loss. This assessment may involve various tests, as mentioned earlier, along with additional evaluations based on individual needs. Adults may also benefit from speech therapy or auditory rehabilitation to enhance their communication skills and adapt to the changes caused by hearing loss.
CBD for Tinnitus: Can It Stop the Ringing?
Early Detection: Importance of Timely Diagnosis for Hearing Rehabilitation
Early detection of meningitis-related hearing loss is crucial for initiating timely intervention and maximizing hearing rehabilitation outcomes. Prompt diagnosis allows for the implementation of appropriate treatment options, such as hearing aids, assistive listening devices, or cochlear implants, depending on the severity of the hearing loss. The American Academy of Otolaryngology emphasizes that “early intervention for children with hearing loss can significantly improve speech and language skills, academic achievement, and overall well-being.”
Furthermore, early diagnosis enables the engagement of speech-language pathologists and audiologists who can provide tailored support and rehabilitation strategies. Speech therapy can help individuals develop effective communication skills and strategies to overcome the challenges associated with hearing loss. Rehabilitation programs may also involve auditory training, which focuses on improving the ability to understand and interpret speech sounds.
By prioritizing early detection and seeking timely diagnosis, caregivers can ensure that their loved ones receive the necessary interventions and support to mitigate the impact of meningitis-related hearing loss on their overall communication and quality of life.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, recognizing and diagnosing meningitis-related hearing loss is crucial for empathetic caregivers. By understanding the symptoms associated with hearing loss as a result of meningitis, differentiating between acute and chronic hearing loss, familiarizing ourselves with diagnostic tools and tests, evaluating hearing loss in both children and adults, and emphasizing the importance of early detection, we can ensure timely intervention and support for our loved ones.
Early detection plays a pivotal role in hearing rehabilitation, as it allows for the implementation of appropriate interventions, such as hearing aids or cochlear implants, and enables access to speech therapy and auditory training. By seeking timely diagnosis and engaging with healthcare professionals, caregivers can empower their loved ones to overcome communication barriers and lead fulfilling lives.
Remember, as an empathetic caregiver, you play a vital role in advocating for your loved ones’ hearing health. Stay vigilant for any signs of hearing loss, especially in individuals who have experienced meningitis. Promptly consult with healthcare professionals, such as audiologists and otolaryngologists, to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
By being proactive in recognizing and diagnosing meningitis-related hearing loss, you can provide the necessary support, resources, and rehabilitation to empower your loved ones on their journey towards improved communication and quality of life.

Unveiling the Financial Landscape of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
93 / 100 Introduction As we open the dialogue on sensorineural hearing loss, it’s essential to understand the weight of this health condition not only

Unraveling the Societal Threads of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: An In-depth Analysis
93 / 100 Introduction Sensorineural hearing loss, while being a medical condition, intersects numerous societal dynamics, shaping the lived experiences of those affected, particularly seniors.